Drs. Anz, Hackel, Nilssen, and Andrews authored an article regarding the application of biologics in sports medicine which was published this month in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgery.
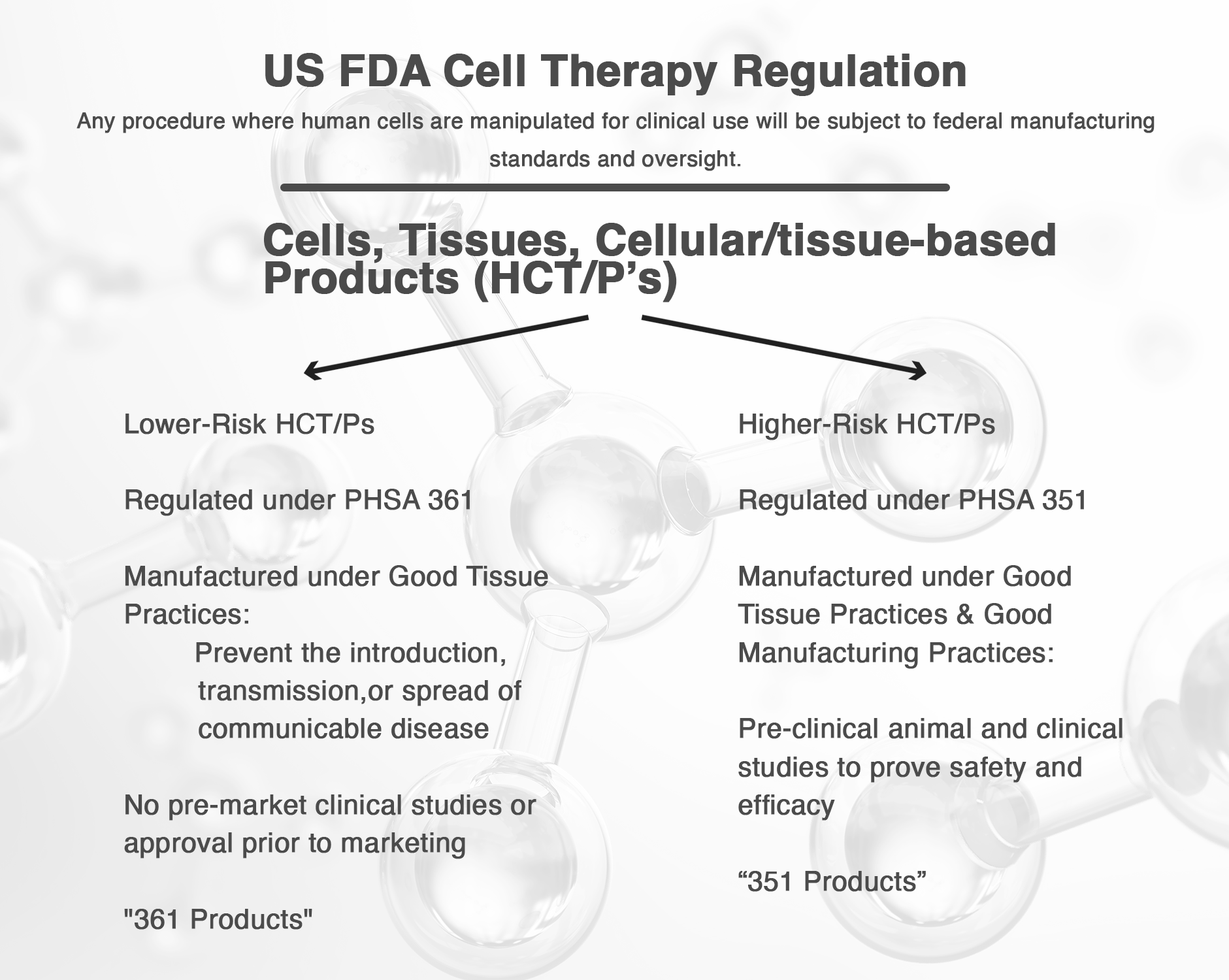
The article entitled “Application of biologics in the treatment of the rotator cuff, meniscus, cartilage, and osteoarthritis” reviewed the current status of the use of platelet-rich plasma, bone marrow aspirate, and stem cells within sports medicine.
What can stem cells do?
There is evidence that these technologies are going to influence the way that orthopaedic surgeons practice medicine, and work at the Andrews Institute is focusing on leading the way but also producing proof that these methods are making a difference in the lives of our patients.