Stem Cells are cells in our bodies as children and adults which are important for the growth and healing potential of our body. These cells are one generation from some of the youngest cells present when we are developing in the womb, as an embryo. These stem cells can be found in multiple area of the body as adults and are named based upon the location where they can be obtained.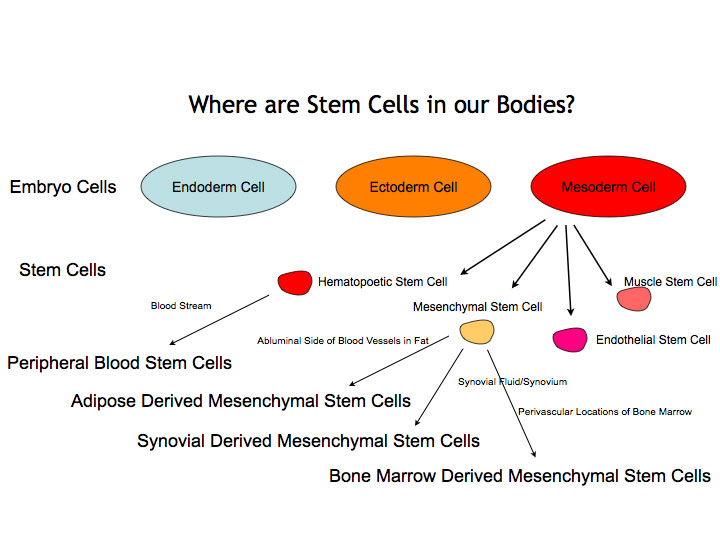
Stem cells have the ability to perform four functions which are important for regenerative potential: the ability to reproduce (proliferatory potential), the ability to differentiate and mature into a different number of cell lines (multipotentiality), the ability to mobilize in situations of blood vessel formation, and the ability to activate and control cells within their environment (trophic functions). Although all four of these functions can be used to the advantage of regenerative medicine, most scientists have sought to utilize the ability of stem cells to mature into a cell needed for repair. Stem cells also have ability to release growth factors and signaling molecules at a region of healing. For orthopaedic purposes, the mesenchymal stem cell has garnered the most interest due to its direct path to change into cells important for orthopaedic purposes.
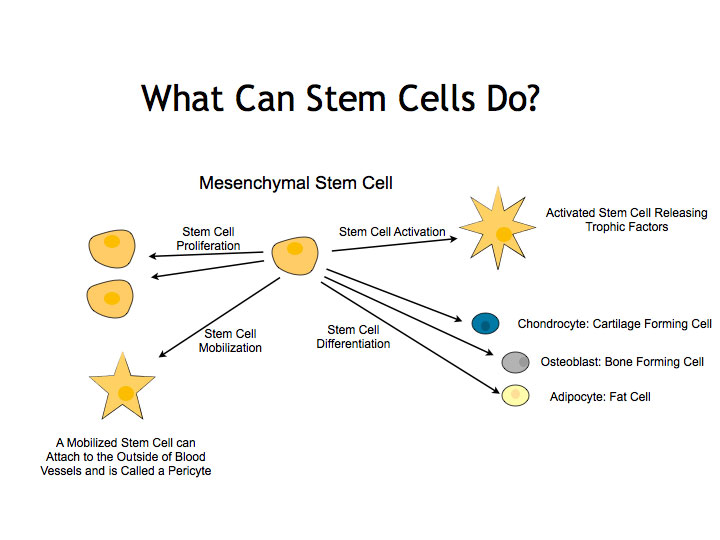 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from the bone marrow, lining of a joint (synovial tissue), lining around bones (periosteum), and fat. Cells obtained from different sites are slightly different. The peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) is a cell that which is present within the blood stream and originates from the bone marrow. In laboratory studies, bone marrow derived, adipose derived, periosteum derived, and synovial derived MSCs as well as PBSCs have illustrated the ability to turn into bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. Additionally, scientists have been able to turn bone marrow derived MSCs and PBSCs into brain cells, heart cells, and liver cells in laboratory study.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from the bone marrow, lining of a joint (synovial tissue), lining around bones (periosteum), and fat. Cells obtained from different sites are slightly different. The peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) is a cell that which is present within the blood stream and originates from the bone marrow. In laboratory studies, bone marrow derived, adipose derived, periosteum derived, and synovial derived MSCs as well as PBSCs have illustrated the ability to turn into bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. Additionally, scientists have been able to turn bone marrow derived MSCs and PBSCs into brain cells, heart cells, and liver cells in laboratory study.
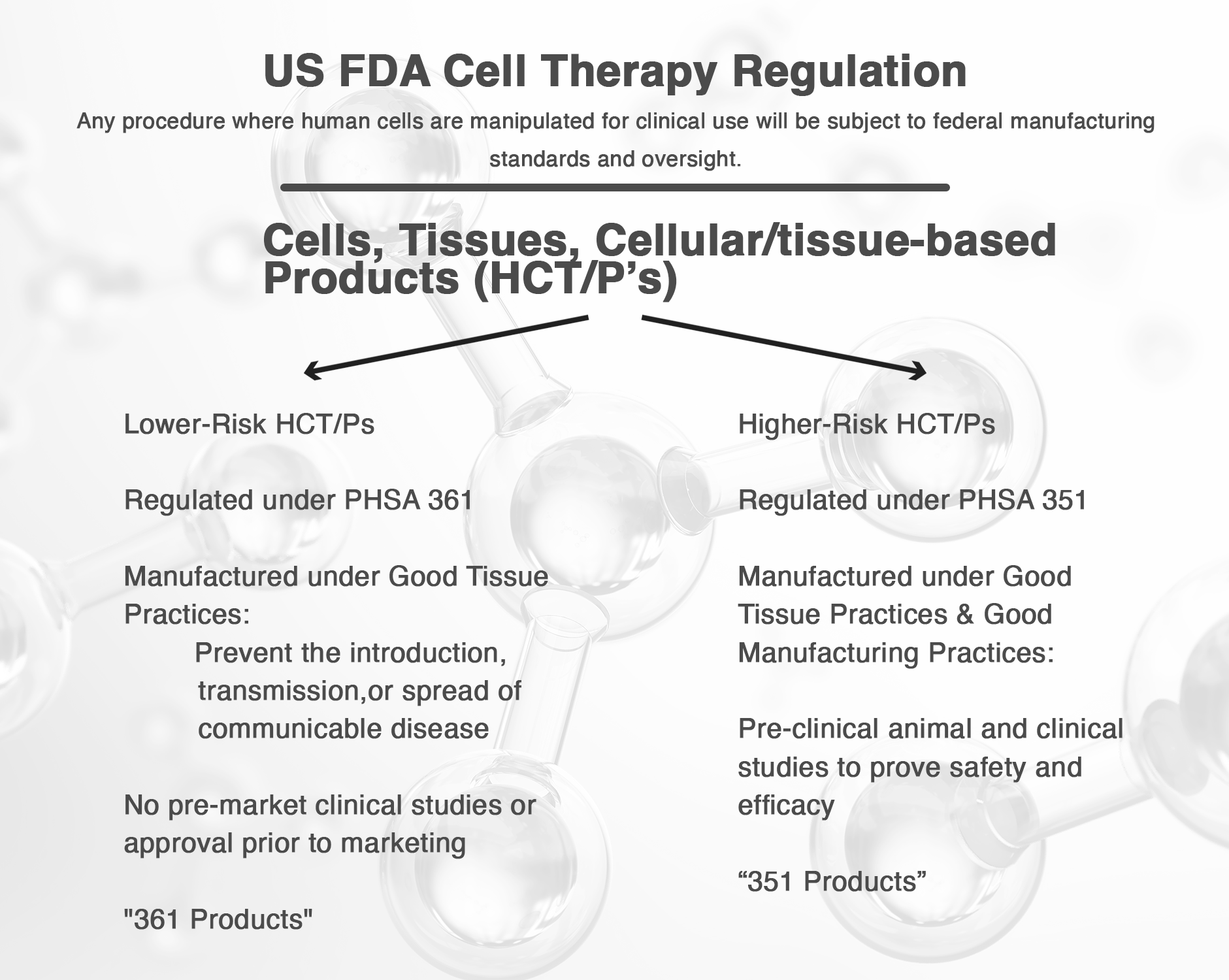
Progress with stem cells has been exciting in scientific laboratories and animal studies. However, some work is still required to apply what we have learned to patient care on a daily basis. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of stem cells to treat patients. They have set up mechanisms to ensure that treatments utilizing stem cells are safe and useful for patients. Treatments involving bone marrow aspirate are currently the only stem cell treatments which orthopaedic surgeons can offer patients outside of clinical trials.










 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from the bone marrow, lining of a joint (synovial tissue), lining around bones (periosteum), and fat. Cells obtained from different sites are slightly different. The peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) is a cell that which is present within the blood stream and originates from the bone marrow. In laboratory studies, bone marrow derived, adipose derived, periosteum derived, and synovial derived MSCs as well as PBSCs have illustrated the ability to turn into bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. Additionally, scientists have been able to turn bone marrow derived MSCs and PBSCs into brain cells, heart cells, and liver cells in laboratory study.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from the bone marrow, lining of a joint (synovial tissue), lining around bones (periosteum), and fat. Cells obtained from different sites are slightly different. The peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) is a cell that which is present within the blood stream and originates from the bone marrow. In laboratory studies, bone marrow derived, adipose derived, periosteum derived, and synovial derived MSCs as well as PBSCs have illustrated the ability to turn into bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. Additionally, scientists have been able to turn bone marrow derived MSCs and PBSCs into brain cells, heart cells, and liver cells in laboratory study.